「算法刷题」链表相关经典题目
一、
顺序结构:这里主要指的是数组或字符串。
一、链表的基本操作
| LeetCode题目 | 相关题目类型 | 相关链接 |
|---|---|---|
| 707 | 设计链表(中等难度) | https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/design-linked-list/ |
在链表中添加或删除元素时,记得修改链表长度;
代码:csdn博客:力扣 707. 设计链表 链表
1 | class MyLinkedList { |
二、链表的相交
| LeetCode题目 | 相关题目类型 | 关键点 | 相关链接 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 面试题02.07. | 链表相交(简单难度) | 长链表的遍历节点先多走和短链表的长度差个节点,然后同时遍历两个节点比较是否存在相同节点 | https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci/ |
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci/solution/dai-ma-sui-xiang-lu-dai-ni-gao-ding-lian-5ykc/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
交点不是数值相等,而是指针相等。
看如下两个链表,目前curA指向链表A的头结点,curB指向链表B的头结点:
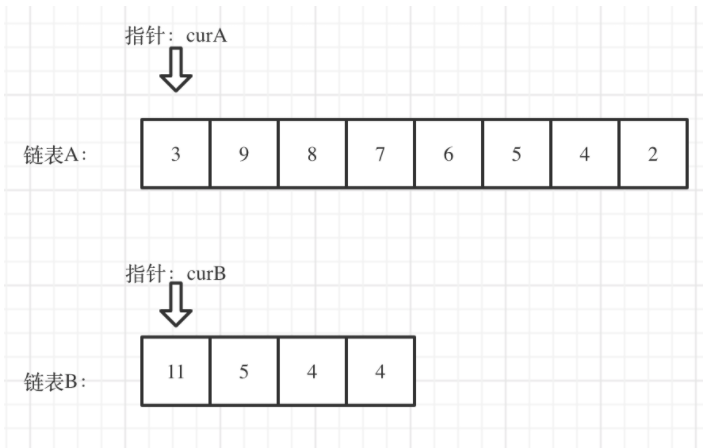
我们求出两个链表的长度,并求出两个链表长度的差值,然后让curA移动到,和curB 末尾对齐的位置,如图:
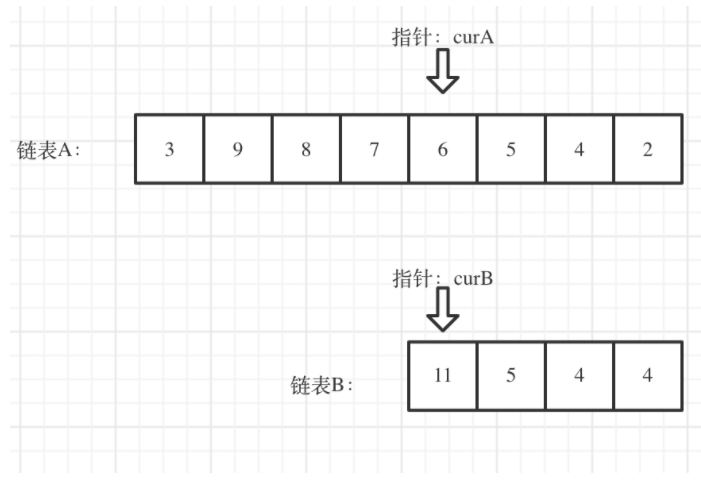
此时我们就可以比较curA和curB是否相同,如果不相同,同时向后移动curA和curB,如果遇到curA == curB,则找到焦点。
否则循环退出返回空指针。
作者:carlsun-2
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci/solution/dai-ma-sui-xiang-lu-dai-ni-gao-ding-lian-5ykc/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
1 | /** |
| LeetCode题目 | 相关题目类型 | 关键点 | 相关链接 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 92 | 反转链表2(中等难度) | 长链表的遍历节点先多走和短链表的长度差个节点,然后同时遍历两个节点比较是否存在相同节点 | 92. 反转链表 II - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com) |
解题思路:
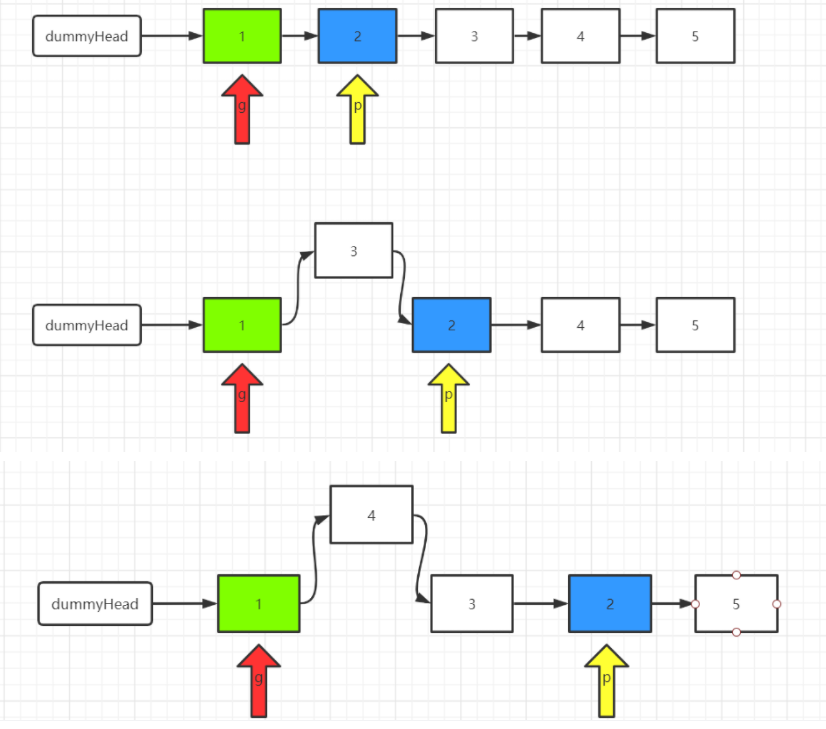
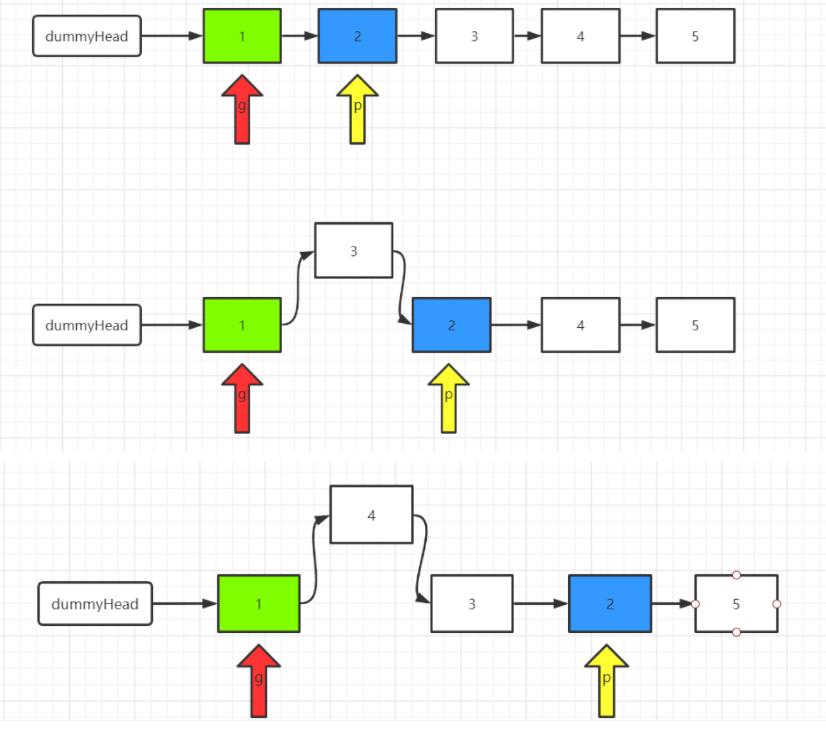
1、我们定义两个指针,分别称之为 g(guard 守卫) 和 p(point)。
我们首先根据方法的参数 m 确定 g 和 p 的位置。将 g 移动到第一个要反转的节点的前面,将 p 移动到第一个要反转的节点的位置上。我们以 m=2,n=4为例。
2、将 p 后面的元素删除,然后添加到 g 的后面。也即头插法。
3、根据 m 和 n 重复步骤(2)
4、返回 dummyHead.next
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/solution/java-shuang-zhi-zhen-tou-cha-fa-by-mu-yi-cheng-zho/
1 | class Solution { |
| LeetCode题目 | 相关题目类型 | 关键点 | 相关链接 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 142 | 环形链表2(中等难度) | 142. 环形链表 II - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com) |
思路
主要考察两知识点:
判断链表是否环
如果有环,如何找到这个环的入口
判断链表是否有环
可以使用快慢指针法, 分别定义 fast 和 slow指针,从头结点出发,fast指针每次移动两个节点,slow指针每次移动一个节点,如果 fast 和 slow指针在途中相遇 ,说明这个链表有环。
为什么fast 走两个节点,slow走一个节点,有环的话,一定会在环内相遇呢,而不是永远的错开呢
首先第一点: fast指针一定先进入环中,如果fast 指针和slow指针相遇的话,一定是在环中相遇,这是毋庸置疑的。
那么来看一下,为什么fast指针和slow指针一定会相遇呢?
可以画一个环,然后让 fast指针在任意一个节点开始追赶slow指针。
会发现最终都是这种情况, 如下图:

ast和slow各自再走一步, fast和slow就相遇了
这是因为fast是走两步,slow是走一步,其实相对于slow来说,fast是一个节点一个节点的靠近slow的,所以fast一定可以和slow重合。
如果有环,如何找到这个环的入口
此时已经可以判断链表是否有环了,那么接下来要找这个环的入口了。
假设从头结点到环形入口节点 的节点数为x。
环形入口节点到 fast指针与slow指针相遇节点 节点数为y。
从相遇节点 再到环形入口节点节点数为 z。 如图所示:

那么相遇时:
slow指针走过的节点数为: x + y,
fast指针走过的节点数: x + y + n (y + z),n为fast指针在环内走了n圈才遇到slow指针, (y+z)为 一圈内节点的个数A。
因为fast指针是一步走两个节点,slow指针一步走一个节点, 所以 fast指针走过的节点数 = slow指针走过的节点数 * 2:
(x + y) * 2 = x + y + n (y + z)
两边消掉一个(x+y): x + y = n (y + z)
因为要找环形的入口,那么要求的是x,因为x表示 头结点到 环形入口节点的的距离。
以要求x ,将x单独放在左面:x = n (y + z) - y ,
再从n(y+z)中提出一个 (y+z)来,整理公式之后为如下公式:x = (n - 1) (y + z) + z 注意这里n一定是大于等于1的,因为 fast指针至少要多走一圈才能相遇slow指针。
这个公式说明什么呢?
先拿n为1的情况来举例,意味着fast指针在环形里转了一圈之后,就遇到了 slow指针了。
当 n为1的时候,公式就化解为 x = z,
这就意味着,从头结点出发一个指针,从相遇节点 也出发一个指针,这两个指针每次只走一个节点, 那么当这两个指针相遇的时候就是 环形入口的节点。
也就是在相遇节点处,定义一个指针index1,在头结点处定一个指针index2。
让index1和index2同时移动,每次移动一个节点, 那么他们相遇的地方就是 环形入口的节点。
那么 n如果大于1是什么情况呢,就是fast指针在环形转n圈之后才遇到 slow指针。
其实这种情况和n为1的时候 效果是一样的,一样可以通过这个方法找到 环形的入口节点,只不过,index1 指针在环里 多转了(n-1)圈,然后再遇到index2,相遇点依然是环形的入口节点。
1 | /** |